Singapore’s manufacturing sector are like a powerful engine, driving the country’s economy forward. The factories come a long way, from making simple things to advanced products used around the world. Over the years, it has evolved from low-cost production to high-value manufacturing, propelling Singapore into the ranks of global economic powerhouses.
According to data from the Singapore Department of Statistics (SingStat), the Singapore’s manufacturing sector has played a pivotal role in Singapore’s economic landscape, contributing significantly to its Gross Domestic Product (GDP) and employment (Source: SingStat, 2024).
As per Statista, Singapore’s manufacturing GDP growth reflects the sector’s historical significance, showcasing a transition toward more advanced manufacturing capabilities.
What Makes Singapore’s Manufacturing Special?
The country’s economic success story is intricately linked to its thriving Singapore’s manufacturing sector. Standing as a key driver of the economy, it has contributed substantially to the nation’s growth. Singapore used to focus on making things cheaply, but now they’re all about high-quality, innovative products.
Key Features of Manufacturing Landscape
Prominent Sectors
Singapore’s manufacturing landscape is diverse, with several key sectors driving its economic engine. The electronics industry reigns supreme, with Singapore serving as a hub for semiconductor manufacturing, precision engineering, and electronics components.
These factories create tons of jobs for people of all skill levels, from engineers to machine operators. It’s like having a giant team working together to keep the economy strong.
- Electronics

This sector is the backbone of Singapore’s manufacturing industry, which includes the production of semiconductors, integrated circuits and electronic components. The country contributes significantly to the country’s exports and attracts leading multinational companies due to its advanced infrastructure and skilled workforce.
- Chemicals

Singapore has a well-developed chemicals sector, with a focus on specialty chemicals, petrochemicals and pharmaceuticals. This sector plays an important role in supporting other industries and contributing to research and development (R&D) activities.
- Biomedical Sciences

This fast-growing sector focuses on areas such as medical technology, pharmaceuticals and biotechnology. It has huge potential for future growth backed by strong government support and research and development initiatives.
- Precision Engineering
 This sector includes the production of high-precision components and machines used in various industries such as aerospace, electronics and healthcare. The company leverages advanced technology and a skilled workforce to meet the demands of the high-value market.
This sector includes the production of high-precision components and machines used in various industries such as aerospace, electronics and healthcare. The company leverages advanced technology and a skilled workforce to meet the demands of the high-value market.
Contribution to the Economy
Singapore is embracing the change and investing in new technology and training to keep their factories ahead. They also collaborate with other countries in the region to open new markets and share ideas.
According to Statista, the manufacturing sector remains a significant contributor to Singapore’s economy, accounting for approximately 20% of the GDP. This economic contribution translates into substantial job creation (Source: Statista, 2024).
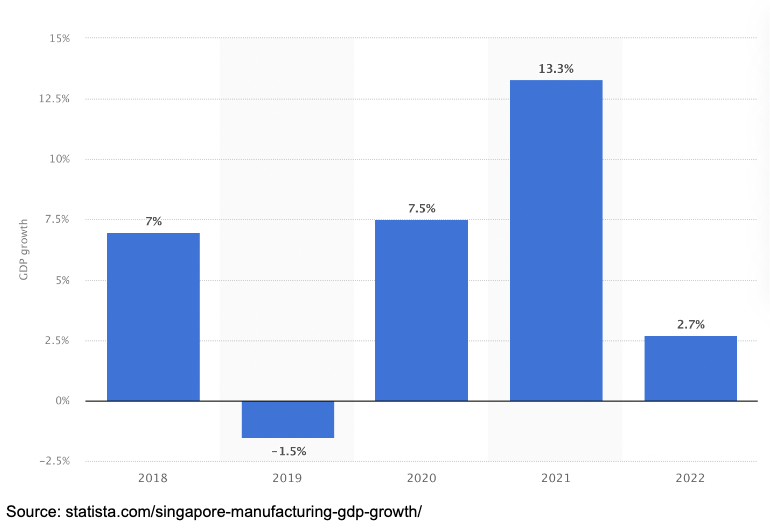
Beyond GDP, the manufacturing sector plays an important role in job creation, offering a wide range of employment opportunities at various skill levels. From skilled technicians to research scientists, the sector drives talent development and job creation.
Challenges in Manufacturing Sectors
Singapore’s manufacturing sector faces several significant challenges. These challenges can be broadly categorized into internal and external factors, which demand adaptation and resilience from industry players (Source: Singapore Business, 2018).
Internal Challenges:
- Rising Costs: Manufacturers in Singapore are grappling with rising land, labor and raw material costs. Continued pressure on margins may limit their ability to compete in global markets.
- Workforce Skills Gap: Rapid technological progress in the manufacturing sector which is driven by Industry 4.0 requires a workforce equipped with relevant skills. However, the existing workforce may not have these skills, creating a talent gap.
- Legacy Infrastructure: Some manufacturers still rely on outdated equipment and infrastructure, hampering their efficiency and productivity compared to competitors who have adopted new technology.
External Challenges:
- Global Competition: Singapore’s small domestic market requires its producers to actively participate in the global market. This makes them face stiff competition from countries with lower labor costs or government subsidies.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: The COVID-19 pandemic and recent geopolitical tensions have highlighted the fragility of global supply chains. Manufacturers in Singapore, which rely heavily on imports and exports, are vulnerable to disruptions in this chain, impacting production and delivery schedules.
- Economic and Political Instability: The global economic landscape is characterized by instability, with factors such as inflation and trade wars impacting demand and costs. Additionally, political instability in key regions could disrupt trade flows, creating further challenges for producers.
The Opportunities
As the largest contributor to GDP (exceeding 20%) and having an important position as the 5th largest exporter of high-tech goods globally, the manufacturing sector continues to provide attractive opportunities for businesses and individuals (Source: MTI Singapore, 2023).
- Embracing Industry 4.0
One of the main drivers of this success story is Singapore’s proactive approach to Industry 4.0 (Source: EDB Singapore, 2024). The country is actively integrating technologies such as automation, artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things (IoT) into its manufacturing processes. This not only increases efficiency and productivity but also drives the sector towards high-value production.
- A Diverse Landscape
The Singaporean manufacturing sector is far from monolithic. A diversified landscape offers opportunities across various sub-sectors, while electronics remain a bedrock and contribute around 8% of the GDP (Source: MOE Singapore, 2024).
- A Government Supportive of Growth
The Singaporean government actively supports the manufacturing sector through various initiatives. These include:
- The Singapore Economic Development Board (EDB): Provides targeted assistance to companies establishing or expanding operations in Singapore.
- Manufacturing 2030: This national initiative aims to transform the sector into a globally competitive and sustainable driver of economic growth.
Singapore has a highly skilled and adaptable workforce, and is ranked 2nd in the 2022 Global Talent Competitiveness Index. Through national initiatives such as the SkillsFuture Series in Advanced Manufacturing, the Singapore Government continues to work closely with industry players and higher education institutions.
Top Import Company in Singapore’s Manufacturing Sector
Singapore’s manufacturing sector is a key pillar of its economy, making a significant contribution to GDP and employment opportunities. Export and import is vital to the manufacturing sector in Singapore, driving the production of advanced products and driving economic growth.
Blueray Cargo Singapore specializes in importing goods from China and Thailand, offering reliable freight forwarding services to ensure smooth import operations. The process of sending goods from abroad will be easier with us, cheaper and of course safer.
Starting from the payment process to delivery, it tends to be fast, with a system that has been tested among thousands of business people. The products you order will be stored and processed properly in our warehouse. Contact us now!
Sources:
- Singapore Business Review “TOP CHALLENGES FACED BY SEA MANUFACTURERS TODAY”
https://sbr.com.sg/manufacturing/commentary/top-challenges-faced-sea-manufacturers-today - Statista “Growth of the gross domestic product (GDP) from manufacturing sector in Singapore from 2018 to 2022”
https://www.singstat.gov.sg/find-data/search-by-theme/industry/manufacturing - Ministry of Trade and Industry
https://www.mti.gov.sg/ - EDB Singapore “Transform manufacturing through Industry 4.0”
https://www.edb.gov.sg/en/our-industries/advanced-manufacturing.html - Ministry of Education
https://www.moe.gov.sg/sgis/sponsoring-organisations/industries/electronics















